As the electric vehicle (EV) industry continues its rapid expansion, the demand for robust and efficient charging infrastructure becomes increasingly critical, especially within industrial settings. Factories, with their fleets of electric forklifts, trucks, and other machinery, require reliable charging solutions to maintain operational efficiency and support sustainability goals. Among the various charging standards available, the Type 2 EV Cable has emerged as a preferred choice for factory-level applications due to its versatility, effic
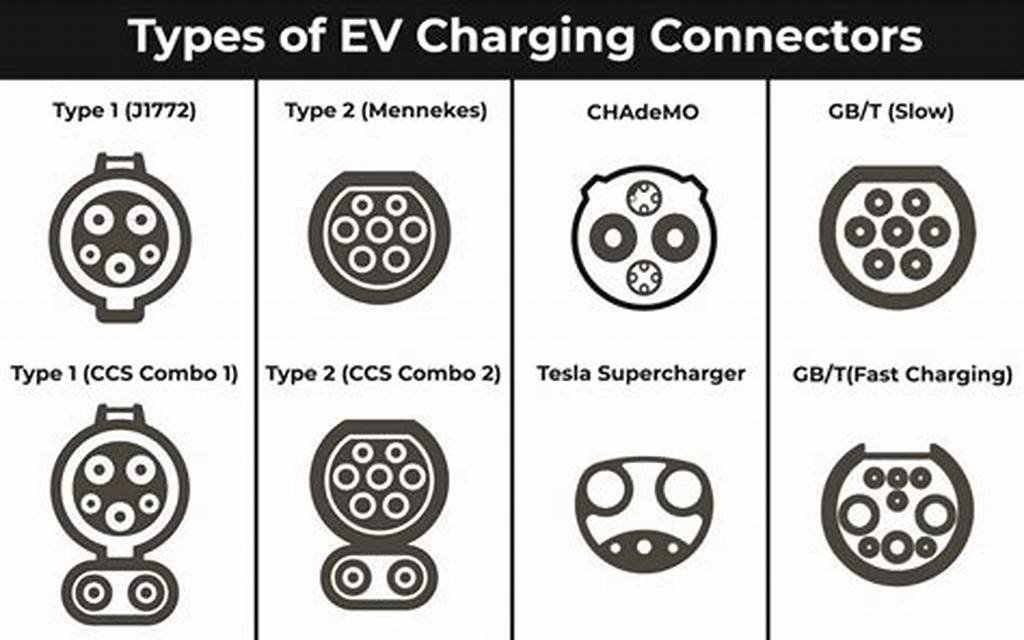
Understanding Type 2 EV Cables for Industrial Use
What is a Type 2 EV Cable?
The Type 2 EV Cable, also known as the Mennekes connector, is a standardized charging connector
Key Specifications
- Voltage and Current: Supports up to 400V and 63A, allowing for faster chargin
- Power Delivery: Capable of delivering up to 22 kW in three-phase mode, significantly reducing charging times for heavy-
- Connector Design: Features a circular design with seven pins, includin
- Safety Features: Equipped with protective shutters and grounding mechanisms to ensure safe and secure connections.
Comparison with Other Charging Standards
| Feature | Type 1 | Type 2 | CCS (Combined Charging System) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region | North America, Japan | Europe, Glob | Europe, North America, As |
| Phase Support | Single-phase | Single and three-phase | Single and three-phase |
| Maximum Power | 7.4 kW | 22 kW | 350 kW |
| Connector Design | Five-pin | Seven-pin | Combination of Type 1/Type 2 |
| Usage in Factories | Limited | Widely adopted | Emerging |
The Type 2 connector’s ability to support higher power levels and three-phase charging makes it particularly suitable for factory environments, where rapid and efficient charging of multiple vehicles is essential.
Benefits of Type 2 EV Cables in Factory Settings
Implementing Type 2 EV Cables within factory operations offers numerous advantages that enhance productivity, sustainability, and cost-efficiency.
1. Enhanced Charging Efficiency
Type 2 EV Cables support three-phase power, enabling significantly faster charging times compared to single-phase alternatives. For instance, a three-phase Type 2 charger can deliver up to 22 kW, allowing electric forklifts to charge in under an hour. This rapid turnaround is crucial for maintaining operational flow and minimizing downtime.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Factories often operate with fleets of varying sizes and types of electric vehicles. Type 2 EV Cables offer scalability, allowing factories to expand their charging infrastructure as their fleet grows. The standardized design ensures compatibility with a wide range of EV models, providing flexibility in fleet management.
3. Reliability and Durability
Industrial environments are harsh, with exposure to dust, moisture, and heavy usage. Type 2 EV Cables are built to withstand such conditions, featuring robust materials and protective coatings. This durability ensures a long lifespan and reduces the need for frequent replacements, thereby lowering maintenance costs.
4. Compliance with International Standards
Adhering to international safety and performance standards is paramount in factory settings. Type 2 EV Cables comply with IEC 62196-2 and other relevant standards, ensuring safe and reliable operation. This compliance not only enhances safety but also facilitates easier integration with existing electrical systems and infrastructure.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in Type 2 EV Charging infrastructure may be higher than lower-powered alternatives, the long-term savings are substantial. Faster charging reduces labor costs associated with downtime, and the durable construction minimizes maintenance and replacement expenses. Additionally, many governments offer incentives and rebates for adopting sustainable technologies, further offsetting costs.
6. Environmental Sustainability
Implementing Type 2 EV Cables aligns with global sustainability goals. By enabling the efficient use of electric fleets, factories can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. Moreover, integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, with Type 2 EV Charging systems can enhance environmental benefits, promoting a greener industrial operation.
Factory-Level EV Charging Infrastructure
A comprehensive EV charging infrastructure in factories involves more than just installing Type 2 EV Cables. It requires strategic planning, integration with existing systems, and the incorporation of smart technologies to optimize performance and energy usage.
Components of Factory EV Charging Infrastructure
- Charging Stations: Industrial-grade Type 2 chargers that can handle high power outputs and multiple vehicles simultaneously.
- Electrical Infrastructure: Upgraded electrical panels and dedicated circuits to support the increased power demand.
- Smart Management Systems: Software solutions that monitor and manage charging sessions, optimize energy distribution, and provide real-time data analytics.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Solar panels or other renewable sources that supplement the grid power, enhancing sustainability and reducing energy costs.
- Energy Storage Systems: Batteries or other storage solutions that store excess energy generated from renewable sources for use during peak demand periods.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: Systems that allow electric vehicles to feed energy back into the grid, providing additional energy resilience and flexibility.
Integration with Existing Electrical Systems
Integrating Type 2 EV Charging infrastructure with existing factory electrical systems requires careful planning and execution. Key considerations include:
- Load Assessment: Conducting a thorough load assessment to determine the additional power requirements and ensuring that the existing electrical system can handle the increased demand.
- Circuit Installation: Installing dedicated circuits for EV Charging to prevent overloading and ensure stable power supply.
- Grid Compatibility: Ensuring that the charging infrastructure is compatible with the local grid specifications and regulations.
- Energy Management: Implementing energy management systems that balance the energy load, prioritize charging during off-peak hours, and integrate renewable energy sources effectively.
Importance of Smart Charging Solutions
Smart charging solutions are essential for optimizing energy usage, reducing costs, and enhancing the overall efficiency of the charging infrastructure. These systems offer features such as:
- Load Balancing: Distributing power evenly across multiple chargers to prevent overloading and ensure consistent charging speeds.
- Scheduling: Allowing factories to schedule charging sessions during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, thereby reducing energy costs.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Enabling real-time monitoring and remote control of charging stations through mobile apps or centralized dashboards.
- Data Analytics: Providing insights into energy consumption, charging patterns, and operational efficiency to inform strategic decision-making.
Role of Renewable Energy
Integrating renewable energy sources with Type 2 EV Charging infrastructure offers significant benefits, including:
- Cost Savings: Reducing reliance on grid power by utilizing solar or wind energy can lower operational costs.
- Sustainability: Enhancing the environmental credentials of the factory by using clean energy sources.
- Energy Resilience: Providing backup power through renewable energy integration ensures continuous operation during grid outages or fluctuations.
Designing Factory Solutions with Type 2 EV Cables
Designing an effective factory-level EV Charging solution involves several critical steps, from assessing charging needs to ensuring compliance with safety standards. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the process:
Assessing Charging Needs
Understanding the specific charging requirements of the factory is the first step in designing an effective EV Charging solution. Key factors to consider include:
- Fleet Size and Type: Assessing the number and types of electric vehicles in the fleet to determine the total power demand and the number of charging points required.
- Usage Patterns: Analyzing the daily usage patterns of the fleet to identify peak charging times and optimize charging schedules accordingly.
- Charging Speed Requirements: Determining the required charging speeds based on operational needs, such as the time available for vehicles to charge during shifts.
Planning the Layout and Installation
Strategic planning of the charging station layout ensures efficient use of space and minimizes disruptions to factory operations. Considerations include:
- Proximity to Parking Areas: Installing charging stations near vehicle parking areas to reduce cable lengths and improve accessibility.
- Electrical Infrastructure: Ensuring that charging stations are connected to a robust electrical infrastructure capable of handling the high power demands.
- Safety and Accessibility: Designing the layout to comply with safety regulations and ensuring that charging stations are easily accessible to users without obstructing factory workflows.
Choosing the Right Type 2 EV Cables and Chargers
Selecting the appropriate Type 2 EV Cables and chargers is crucial for meeting the factory’s specific needs. Factors to consider include:
- Power Rating: Choosing chargers with suitable power ratings (e.g., 22 kW) to meet the desired charging speeds and handle the fleet size.
- Durability: Selecting cables and chargers designed for industrial environments, featuring robust construction and weather-resistant materials.
- Smart Features: Opting for chargers with smart capabilities, such as load balancing, scheduling, and remote monitoring, to enhance operational efficiency.
- Compatibility: Ensuring that the chosen Type 2 EV Cables are compatible with the factory’s electric vehicles and the charging infrastructure.
Compliance with Safety and Industry Standards
Adhering to safety and industry standards is imperative to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the EV Charging infrastructure. Key standards include:
- IEC 62196-2: Defines the specifications for Type 2 connectors, ensuring interoperability and safety.
- UL 2202: Certification for EV charging systems, ensuring compliance with North American safety standards.
- Local Electrical Codes: Complying with regional electrical codes and regulations to ensure lawful and safe installations.
Case Studies and Examples
Examining real-world implementations can provide valuable insights into effective factory-level EV Charging solutions. Here are two illustrative examples:
Case Study 1: Siemens Manufacturing Plant
Background: Siemens, a global leader in industrial manufacturing, sought to electrify its fleet of forklifts to enhance sustainability and reduce operational costs.
Solution:
- Installation of 20 Type 2 EV Chargers: Each capable of delivering 22 kW, strategically placed near forklift parking areas.
- Integration with Solar Panels: Siemens installed a 100 kW solar panel array to power the charging stations, supplemented by the grid during peak demand.
- Smart Charging Management: Implemented a centralized management system to monitor and optimize charging schedules based on solar energy availability and grid rates.
Results:
- Reduced Energy Costs: Achieved a 30% reduction in energy expenses through optimized charging and solar integration.
- Increased Fleet Efficiency: Reduced charging times by 50%, allowing for continuous forklift operation without significant downtime.
- Sustainability Goals Met: Lowered carbon emissions by approximately 40 tons annually by switching to electric forklifts and using renewable energy sources.
Case Study 2: Toyota Motor Manufacturing
Background: Toyota’s manufacturing facility aimed to support its growing fleet of electric vehicles with a reliable and scalable charging infrastructure.
Solution:
- Deployment of 50 Type 2 EV Chargers: Installed across multiple locations within the factory to accommodate a fleet of 200 electric vehicles.
- Energy Storage System: Integrated a 500 kWh battery storage system to manage energy load and provide backup power during grid outages.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Utilized advanced data analytics to track energy usage, charging patterns, and operational efficiency, informing continuous improvements.
Results:
- Operational Reliability: Ensured uninterrupted charging during grid outages, maintaining fleet availability and production continuity.
- Energy Optimization: Improved energy efficiency by 25% through intelligent load management and peak demand reduction.
- Enhanced Reporting: Gained actionable insights from data analytics, enabling informed decision-making and proactive maintenance.
Implementation Strategies
Successfully implementing Type 2 EV Cable solutions in factories requires a strategic approach that encompasses planning, execution, and ongoing management. Here’s a step-by-step guide to effective implementation:
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Needs Assessment
Begin by evaluating the factory’s specific requirements to tailor the EV Charging solution accordingly:
- Fleet Analysis: Determine the number and types of electric vehicles, their usage patterns, and charging needs.
- Electrical Capacity: Assess the existing electrical infrastructure to identify necessary upgrades and ensure it can support the additional load.
- Future Growth: Consider potential fleet expansion and scalability of the charging infrastructure to accommodate future needs.
2. Develop a Detailed Implementation Plan
Create a comprehensive plan that outlines all aspects of the installation process:
- Timeline: Establish a realistic timeline for each phase of the project, including planning, procurement, installation, and testing.
- Budget: Define a clear budget that covers equipment costs, installation fees, permits, and any necessary electrical upgrades.
- Resource Allocation: Assign responsibilities to team members and identify any external partners or contractors needed for the project.
3. Select Reliable Suppliers and Partners
Partnering with reputable suppliers and service providers is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of the EV Charging infrastructure:
- Charger Manufacturers: Choose established manufacturers known for producing high-quality Type 2 EV Chargers with robust warranties and support.
- Electrical Contractors: Engage certified electrical contractors with experience in industrial installations to handle the electrical work safely and efficiently.
- Technology Providers: Collaborate with technology providers that offer smart management systems and integration services for seamless operation.
4. Execute the Installation
Implement the plan with precision, adhering to safety standards and best practices:
- Site Preparation: Prepare the installation sites by ensuring they are accessible, safe, and conducive to efficient charging operations.
- Charger Installation: Mount the Type 2 EV Chargers securely, ensuring they are easily accessible to vehicles and compatible with the factory’s layout.
- Electrical Connections: Install dedicated circuits and ensure all electrical connections comply with safety regulations and industry standards.
- Integration with Smart Systems: Configure smart management systems to monitor and control the charging infrastructure effectively.
5. Conduct Thorough Testing and Commissioning
Before fully operationalizing the charging infrastructure, perform comprehensive testing to ensure everything functions correctly:
- Functional Testing: Verify that each charger operates as intended, delivering the correct power levels and facilitating seamless communication with vehicles.
- Safety Checks: Conduct safety inspections to ensure all installations meet regulatory requirements and safety standards.
- Performance Evaluation: Assess the overall performance of the charging infrastructure, identifying and addressing any issues or inefficiencies.
6. Provide Training and Support
Equip factory staff with the knowledge and skills needed to operate and maintain the EV Charging infrastructure:
- Training Programs: Offer training sessions on how to use the charging stations, manage energy usage, and troubleshoot common issues.
- Documentation: Provide comprehensive user manuals and troubleshooting guides to assist staff in day-to-day operations.
- Ongoing Support: Establish a support system for addressing technical issues, performing regular maintenance, and implementing upgrades as needed.
7. Monitor, Analyze, and Optimize
Continuous monitoring and analysis are essential for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of the EV Charging infrastructure:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Utilize smart management systems to monitor charging sessions, energy consumption, and system performance in real-time.
- Data Analytics: Analyze collected data to identify trends, optimize charging schedules, and improve energy management strategies.
- Performance Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews to assess the impact of the charging infrastructure on operational efficiency and sustainability goals.
Market Data and Analysis
Global EV Market Growth
The global electric vehicle market has witnessed exponential growth over the past decade. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the number of electric cars on the road surpassed 10 million in 2020 and is projected to reach 145 million by 2030. This surge is driven by advancements in battery technology, decreasing costs, and supportive government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
Industrial EV Adoption
The industrial sector is increasingly adopting electric vehicles to enhance operational efficiency and meet sustainability targets. A report by ResearchAndMarkets.com indicates that the global electric industrial vehicle market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.5% from 2021 to 2028, reaching a market size of $28.3 billion by 2028. This growth is fueled by the need for cost-effective and eco-friendly fleet management solutions.
Tesla’s Market Share
Tesla is a dominant player in the EV market, holding approximately 20% of the global EV market share as of 2023. The company’s commitment to innovation, extensive Supercharger network, and strong brand loyalty have cemented its position as a leader in the industry. Tesla’s advancements in charging technology and infrastructure are influencing market standards and pushing competitors to enhance their offerings.
Adoption Rates of Type 2 EV Cables in Factories
The adoption of Type 2 EV Cables in factory settings is robust, particularly in regions with high EV penetration and industrialization. According to a survey by EV Charging Insights, approximately 60% of manufacturing facilities in Europe and North America have integrated Type 2 EV Charging Solutions. Factors influencing adoption include:
- Reliability: Type 2 EV Cables offer consistent performance and durability, essential for industrial operations.
- Efficiency: Faster charging capabilities align with the operational needs of factories, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity.
- Scalability: The ability to scale charging infrastructure as fleets grow makes Type 2 EV Cables a preferred choice for expanding businesses.
Regional Insights
Europe
Europe leads the global EV market, with strong government incentives, stringent emissions regulations, and a high level of industrialization driving adoption. Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and Norway are at the forefront of implementing Type 2 EV Charging Solutions in factories, supported by comprehensive charging networks and renewable energy integration.
North America
North America, particularly the United States and Canada, is witnessing significant growth in industrial EV adoption. Government policies and increasing environmental awareness are encouraging factories to transition to electric fleets. The Type 2 EV Connector is gaining popularity, supported by a growing network of charging infrastructure and technological advancements.
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region, driven by rapid industrialization and urbanization, is emerging as a key market for Type 2 EV Charging Solutions. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are investing heavily in EV infrastructure, with factories adopting electric fleets to enhance sustainability and meet regulatory requirements.
Technical Specifications and Standards
Detailed Technical Specifications
Understanding the technical specifications of Type 2 EV Cables is crucial for selecting the right solutions for factory applications. Key specifications include:
- Connector Type: Type 2 (Mennekes) with seven pins, including two for communication.
- Voltage: Up to 400V, supporting high-power charging.
- Current: Up to 63A, allowing for fast charging of heavy-duty vehicles.
- Power Output: Capable of delivering up to 22 kW in three-phase mode.
- Cable Length: Typically available in lengths ranging from 4 meters to 10 meters, providing flexibility in charging station placement.
- Material: High-quality, durable materials with weather-resistant coatings to withstand industrial environments.
- Safety Features: Integrated protective shutters, grounding mechanisms, and automatic shutoff in case of faults.
Relevant Standards
Compliance with international standards ensures the safety, reliability, and interoperability of Type 2 EV Charging Solutions. Key standards include:
- IEC 62196-2: Defines the specifications for Type 2 connectors, ensuring uniformity and compatibility across different manufacturers and regions.
- UL 2202: Certification for EV charging systems in North America, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
- ISO 15118: Protocol for communication between EVs and charging stations, enabling smart charging and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) functionalities.
- RoHS Compliance: Ensures that chargers and cables do not contain hazardous materials, promoting environmental sustainability.
Compatibility with EV Models and Fleets
Type 2 EV Cables are compatible with a wide range of electric vehicles, including passenger cars, commercial trucks, forklifts, and other industrial vehicles. This broad compatibility makes them an ideal choice for factories with diverse fleets. Additionally, the standardization of Type 2 connectors facilitates easier integration with various EV models and charging infrastructure, enhancing operational flexibility.
Smart Features and Connectivity
IoT Integration
Integrating Type 2 EV Charging Solutions with the Internet of Things (IoT) enhances their functionality and operational efficiency. IoT-enabled chargers offer:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Track charging sessions, energy consumption, and charger status in real-time through centralized dashboards.
- Remote Control: Manage and control charging stations remotely via mobile apps or web interfaces, allowing for adjustments without physical intervention.
- Predictive Maintenance: Use data analytics to predict potential issues and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of charging equipment.
Energy Management Systems
Smart energy management systems optimize the use of electrical power within the factory, ensuring efficient and cost-effective charging operations. Features include:
- Load Balancing: Distribute power evenly across multiple chargers to prevent overloading and ensure consistent charging speeds.
- Demand Response: Adjust charging rates based on grid demand and electricity pricing, shifting charging to off-peak hours to reduce costs.
- Renewable Integration: Seamlessly integrate with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to utilize clean energy for EV charging.
Data Analytics
Advanced data analytics provide valuable insights into the performance and efficiency of the charging infrastructure. Key applications include:
- Usage Patterns: Analyze charging habits and peak usage times to optimize charging schedules and energy distribution.
- Operational Efficiency: Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the charging process, enabling targeted improvements.
- Performance Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as energy consumption, charging speed, and operational uptime to assess the effectiveness of the charging solution.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Remote monitoring and control capabilities empower factory managers to oversee and manage the EV Charging infrastructure from anywhere. Benefits include:
- Enhanced Oversight: Monitor multiple charging stations simultaneously, ensuring they are functioning correctly and efficiently.
- Immediate Response: Quickly address any issues or faults detected through remote alerts, minimizing downtime and maintaining operational continuity.
- User Management: Control access to charging stations, set user permissions, and manage charging priorities based on operational needs.
Sustainability and Green Energy Integration
Renewable Energy Sources
Integrating renewable energy sources with Type 2 EV Charging Solutions significantly enhances the sustainability of factory operations. Key benefits include:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Utilizing solar, wind, or other renewable energy sources to power EV Charging reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Independence: Factories can achieve greater energy independence by generating their own clean energy, reducing vulnerability to grid fluctuations and price volatility.
- Cost Savings: Renewable energy integration can lead to substantial long-term cost savings by offsetting energy consumption and reducing utility bills.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology allows electric vehicles to feed energy back into the grid, providing additional benefits for factory operations and the broader energy ecosystem:
- Grid Stability: V2G can help stabilize the grid by supplying energy during peak demand periods, reducing the need for additional power generation.
- Energy Storage: EVs can act as distributed energy storage units, storing excess renewable energy and supplying it back to the grid when needed.
- Revenue Generation: Factories can potentially generate revenue by participating in energy markets and providing grid services through their EV fleets.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Adopting Type 2 EV Charging Solutions aligned with renewable energy integration significantly contributes to carbon footprint reduction:
- Emission Savings: Electric fleets produce zero tailpipe emissions, and when powered by renewable energy, the overall emissions associated with their operation are minimal.
- Sustainability Reporting: Factories can leverage their EV Charging infrastructure to enhance their sustainability reporting, demonstrating commitment to environmental stewardship.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions are implementing stricter emissions regulations, and adopting electric fleets with Type 2 EV Charging ensures compliance with these evolving standards.
Future Trends in Factory-Level EV Charging
Technological Advancements
The future of factory-level EV Charging Solutions is shaped by ongoing technological advancements that enhance efficiency, speed, and functionality:
- Ultra-Fast Charging: Research and development efforts are focused on increasing charging speeds without compromising safety, enabling even quicker turnaround times for electric fleets.
- Wireless Charging: Inductive charging technologies are being explored to eliminate the need for physical cables, offering a more convenient and seamless charging experience.
- Advanced Battery Technologies: Innovations in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, promise higher energy densities and faster charging capabilities, further enhancing the performance of electric fleets.
Emerging Business Models
New business models are emerging to support the widespread adoption of factory-level EV Charging Solutions:
- Subscription-Based Models: Factories can adopt subscription-based models for EV Charging services, providing flexibility and scalability without significant upfront investments.
- Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS): EaaS models offer comprehensive energy management solutions, including EV Charging infrastructure, renewable energy integration, and energy storage systems, as a bundled service.
- Shared Charging Infrastructure: Collaborative initiatives between multiple factories or businesses to share EV Charging infrastructure, optimizing resource utilization and reducing costs.
Innovations in Charging Speed and Capacity
Ongoing innovations are aimed at enhancing the speed and capacity of Type 2 EV Charging Solutions:
- Higher Power Outputs: Development of chargers that can deliver even higher power outputs, reducing charging times and accommodating larger fleets more efficiently.
- Modular Charging Systems: Modular and scalable charging systems that can be easily expanded to meet growing demands without extensive reconfiguration.
- Smart Grid Integration: Enhanced integration with smart grids, allowing for dynamic energy distribution based on real-time demand and supply conditions.
Integration with Smart Cities
As smart cities emerge, factory-level EV Charging Solutions will play a crucial role in the broader urban energy ecosystem:
- Smart Grid Integration: Factories can integrate their EV Charging infrastructure with city-wide smart grids, enabling optimized energy distribution and consumption across different sectors.
- Data-Driven Urban Planning: Data collected from EV Charging infrastructure can inform urban planning and infrastructure development, ensuring that energy resources are utilized efficiently and sustainably.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborations between factories, government entities, and private stakeholders to develop comprehensive EV Charging strategies that support smart city objectives.
Challenges and Solutions
Implementing Type 2 EV Charging Solutions in factories comes with its set of challenges. Addressing these challenges effectively is essential for successful adoption and long-term sustainability.
1. High Initial Investment
Challenge: The upfront costs associated with installing Type 2 EV Charging infrastructure, including chargers, electrical upgrades, and smart management systems, can be substantial.
Solution:
- Government Incentives: Leverage government incentives, rebates, and tax credits available for adopting EV Charging infrastructure, reducing the initial financial burden.
- Financing Options: Explore financing options such as loans, leases, or energy-as-a-service (EaaS) models that spread the costs over time.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Conduct a detailed ROI analysis to demonstrate the long-term cost savings and operational efficiencies gained from the investment.
2. Electrical Infrastructure Limitations
Challenge: Existing electrical infrastructure may not be capable of supporting the high power demands of Type 2 EV Charging solutions.
Solution:
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Collaborate with certified electrical contractors to upgrade the electrical panels, install dedicated circuits, and ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Energy Management Systems: Implement smart energy management systems that optimize power distribution and prevent overloading of the electrical grid.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Integrate renewable energy sources to supplement the electrical supply, reducing the strain on the existing infrastructure.
3. Space Constraints
Challenge: Limited physical space within factory premises can make the installation of EV Charging stations challenging.
Solution:
- Strategic Placement: Optimize the placement of charging stations near vehicle parking areas and minimize cable lengths to efficiently utilize available space.
- Modular Charging Units: Use modular and compact charging units that can be easily scaled and adapted to fit different factory layouts.
- Vertical Installation: Consider vertical mounting options to save floor space and maintain operational workflows.
4. Technical Complexity
Challenge: The technical complexity involved in integrating Type 2 EV Charging Solutions with existing systems and ensuring seamless operation.
Solution:
- Professional Installation: Engage experienced professionals and certified electrical contractors to handle the installation process, ensuring technical accuracy and compliance.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide comprehensive training for factory staff on operating and maintaining the EV Charging infrastructure, reducing reliance on external support.
- Vendor Support: Partner with reputable vendors that offer robust customer support, maintenance services, and regular software updates.
5. Ensuring Reliability and Uptime
Challenge: Maintaining high levels of reliability and uptime for the EV Charging infrastructure to support continuous factory operations.
Solution:
- Redundant Systems: Implement redundant charging systems and backup power solutions to ensure continuous operation even during equipment failures or power outages.
- Regular Maintenance: Establish a regular maintenance schedule to inspect, clean, and service charging equipment, preventing unexpected downtimes.
- Smart Monitoring: Utilize smart monitoring systems to detect and address issues proactively, ensuring optimal performance and minimal disruptions.
Conclusion
The integration of Type 2 EV Cables into factory-level EV Charging Solutions represents a strategic investment that enhances operational efficiency, supports sustainability goals, and aligns with the global shift towards electric mobility. By understanding the technical specifications, benefits, and implementation strategies, factories can effectively adopt and optimize their EV Charging infrastructure to meet their unique needs.
As the EV market continues to grow and evolve, staying abreast of technological advancements and emerging trends will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Embracing smart charging solutions, integrating renewable energy sources, and leveraging data analytics will further enhance the effectiveness and sustainability of factory-level EV Charging Systems.
For factories in the packaging and printing industry, adopting Type 2 EV Charging Solutions not only supports their operational needs but also contributes to broader environmental and economic objectives. By partnering with reliable suppliers, investing in the right technologies, and implementing robust management practices, factories can ensure the successful adoption and long-term success of their EV Charging infrastructure.
To learn more about our comprehensive EV Charging Solutions and how Fisher can help your factory transition to electric mobility, visit our About Us page. Discover how our innovative products and expert support can drive your business forward in the evolving landscape of electric transportation.




